Science topics: Molecular BiologyCOVID-19
Science topic
COVID-19 - Science topic
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness
that can spread from person to person. The virus that causes
COVID-19 is a novel coronavirus that was first identified during
an investigation into an outbreak in Wuhan, China.
Questions related to COVID-19
We are all living in a strange era since last year due to the pandemic of COVID-19, so we are all seeking to find the truth about basic parameters of it.
As everybody knows, any research needs reliable data, so we need data.
But, despite the plethora of available online sets, the critical ones are not always presented publicly.
For example in Greece we do not have online data for next categories, all related to COVID-19:
- daily confirmed cases by vaccination status (vaccinated-partially vaccinated-non vaccinated)
- daily deaths by vaccination status (vaccinated-partially vaccinated-non vaccinated)
In Greece we do not have also next data online:
- number of patients in simple hospital beds or in ICU by vaccination status (3 cases)
- deaths of patients in simple hospital beds or in ICU by vaccination status (3 cases)
The only available set was next:
The webpage is down, but you can see its cached version by Google:
Recently a paper about inside and outside ICU mortality was published with correspondent author having next past jobs
- 2020-02 to 2020-08 | Head of Department (Department of Database Design, Statistics and Data Management)-National Public Health Organization
- 2019-05 to 2020-02 (Office of Scientific Advisors)-National Public Health Organization
- 2017-01 to 2019-05 (Office of Scientific Advisors)-Hellenic Centre for Disease Control and Prevention
- 2014-04 to 2017-01 (Department of Epidemiological Surveillance and Intervention)-Hellenic Centre for Disease Control & Prevention
(All those jobs were at the same Organization, now called "EODY", which is the Greek CDC for all of you that you do not know the Greek reality)
Now we find a paper that uses detailed data from all ICU in Greece.
- Where is the raw data used for that?
- Why nobody else has access to that?
- Is it coming from a Public Organization or not?
Not to make you tired:
- Do you think it is ethical for a scientist to use its exclusively access to COVID-19 data set for making private scientific research?
- Do you agree that all data for COVID-19 that wre collected from public authorities should be open accessed by anyone online?
Thank you for your patient to read such a big test,
I am waiting for your thoughts,
Demetris
How has language, particularly around the unquestionable authority of 'science' (vs. other domains of inquiry that apply rigorous method but are not generally considered 'science') been used to uphold the military industrial complex and other forms of hegemonic rule by global hyper-elites (the top 0.2% of individuals by personal assets)?
A review of public discourse in periods of great turmoil, such as COVID and the rise of NAZI Germany and possible the periods following The French Revolution are places to understand this dynamic. For example, newspapers, online articles, radio, television and public announcement campaigns around particular government policies, election campaigns, or services by private companies.
This is a complex question that incorporates linguistics theory, political science, sociological research methods that are able to scan databases and the internet for appropriate search terms.
To properly answer the question both philosophical models how power operates in the society, Michel Foucault, Manuel Castello and Noam Chomsky are three thinkers with a range of relevant theories along with data-driven approaches to under the true extent to messaging to individual eyes and ears through a broad range of methods of public discourse.
For my project I am looking for the mRNA sequences of mRNA vaccines that are currently undergoing clinical trails or that are already in use. I know that the sequences of two Covid-19 vaccines are publicly available (https://github.com/NAalytics/Assemblies-of-putative-SARS-CoV2-spike-encoding-mRNA-sequences-for-vaccines-BNT-162b2-and-mRNA-1273/blob/main/Assemblies%20of%20putative%20SARS-CoV2-spike-encoding%20mRNA%20sequences%20for%20vaccines%20BNT-162b2%20and%20mRNA-1273.docx.pdf). Would anyone have sequence information of other mRNA vaccines or know where to find it?
In a recent review article titled “N1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ): Beneficial or Harmful for Cancer?” published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, Rubio-Casillas, and colleagues discuss how mRNA vaccines may impact immunological pathways, potentially affecting cancer risk. Their research suggests that a high level of N1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ) in mRNA vaccines could promote cancer growth and metastasis in certain models. This raises concerns about the role of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in cancer development. The authors recommend future clinical trials to explore lower levels of m1Ψ modification to avoid immune suppression.
An earlier study by Professor Abdollah Jafarzadeh and team, published in the International Journal of Hematology-Oncology and Stem Cell Research, explores the potential link between SARS-CoV-2 infection and cancer. They found that cancer patients may have a higher susceptibility to COVID-19 due to their compromised immune systems from cancer treatments. Additionally, recovered COVID-19 patients may experience persistent immune abnormalities that could contribute to cancer development or recurrence.
In my opinion, these studies highlight the complex interactions between COVID-19 and cancer, suggesting a need for further research to understand and address potential risks associated with the pandemic. I would be grateful if you could provide your insightful opinions on this matter.
References:
1. Alberto Rubio-Casillas, David Cowley, Mikolaj Raszek, Vladimir N. Uversky, Elrashdy M. Redwan, Review: N1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ): Friend or foe of cancer?, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024.
2. Jafarzadeh A, Gosain R, Mortazavi SMJ, Nemati M, Jafarzadeh S, Ghaderi A. SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Possible Risk Factor for Incidence and Recurrence of Cancers. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2022;16(2):117-27. doi: 10.18502/ijhoscr.v16i2.9205. PubMed PMID: 36304732. PubMed PMCID: PMC9547773. https://lnkd.in/e8uEbeB7
3. S. M. J. Mortazavi, S. A. Mortazavi, J. S. Welsh and L. Sihver, Journal of Biomedical Physics and Engineering 2023, DOI: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2310-1679 https://lnkd.in/eQCW_MZQ
I want to do phd on mathematical modeling of infectious diseases (eg. Covid 19, maleria, denge). I am also interested in pure mathematics as well like Nonlinear Analysis, Variational Inequalities so my question is can i get any connection between this two part. Need suggestions thank you.
Does anyone knows the pH acceptable range for virus transport medium (VTM) for Sars cov 2 samples? I supose that it depends if you are only testing by PCR or if you need viability for culture but does anyone has experience in this subject?
Found a studie that defends that in normal individuals with no history of reflux or eustachian tube dysfunction, the pH values range from 6.10 to 7.92 with an average pH of 7.03 (SD, 0.67) so i believe that VTM should be buffered around pH 7 (with a variation of plus or minus 1) but need to confirm that.
Thank you and be safe.
Dear Researchers:
Could you please share some simple cures or prevention for COVID-19, Cold, Flu or Influenza, and possibly Other Viruses, and Cancers?
Updates on Oct. 10, 2023: First, many thanks to all contributors to this discussion. Here are some Natural Approaches found from surveying literature in medicine to Boost our Immune Systems against viruses such as COVID-19, Cold, Flu or Influenza infections and to avoid/minimize developing further inflammations in the lungs and hearts caused by some of those viruses:
Give it a try, please! Especially if you increase your Vitamin D level to a required level and consume Vitamin C sources, e.g., oranges, on a daily basis, you can check how rarely you would catch the virus. Or, even after catching the virus, the virus will likely develop very mild symptoms in your body.
1- Daily uptake of Vitamin D pills up to 100 IU per 1 kg weight is safe and very important, recommended by Afshar et al. (2000) and Dr. Hamid Sajjadi in an interview, to RAISE the Vitamin D level in our body to the POINT which is REQUIRED to BOOST our IMMUNE SYSTEMS against Viruses and Diseases including Cancers.
Vitamin D daily use needs to be adjusted based on our body weight.
Please read the following article by Afshar et al. (2000) about the importance of vitamin D and the required daily dose of it (Up to 100 IU per 1 kg weight) to boost our Immune Systems.
Please also read the following Review article by Jordan et al. (2022) about the importance of Vitamin D on the level of infection & disease progression for COVID-19. You may find in the article the importance of our Forgotten SUN.
Vitamin D is rarely available in food sources, except in fatty fish which needs to be eaten high enough to get the required amount of Vitamin D for a body.
Another good natural source is daily sunbathing with naked skin; however, in cloudy regions such as Europe, sunbathing doesn't work well.
Vitamin D helps to absorb Calcium in our intestines and thus, in order to avoid excessive absorption of Calcium by our body, it would be better to use Vitamin D pills with Calcium sources such as warmed-up milk and Magnesium sources such as bananas on a daily basis. Because magnesium competes with calcium in our intestines to get absorbed.
Here is a text from A Review article by Kulie et al. (2009) about some of the importance of Vitamin D on our health:
"Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays an important role in Bone Metabolism and seems to have some Anti-Inflammatory and Immune-Modulating properties. In addition, recent epidemiologic studies have observed relationships between low vitamin D levels and multiple disease states.
Low vitamin D levels are associated with increased overall and Cardiovascular mortality, Cancer incidence and mortality, and Autoimmune Diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis. Although it is well known that the combination of vitamin D and calcium is necessary to maintain Bone Density as people age, vitamin D may also be an independent risk factor for falls among the Elderly."
2- Having Good Nutrients including Protein sources, Minerals, and Other Vitamins, e.g., C, A, and E, sources from fresh fruits, vegetables, and nuts. For example, the good sources of fruits and vegetables for these vitamins could be a daily use of 1-2 Oranges for Vitamin C, Carrots for Vitamin A, and Almonds or Sunflower Seeds for Vitamin E.
As Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, the excess of it will be excreted from the body, it needs to be consumed every day to provide everyday vitamin C requirements for the body, as it is the 2nd most important vitamin after Vitamin D to boost our Immune Systems against viruses and diseases.
And, Vitamin B family from grains, poultry, and meat sources.
3- After the infection by those viruses, gargling salty water to disinfect the throat to avoid further movement of the virus into the lungs as the virus may stay in the throat for a few days
4- Inhaling Steamed Fresh Leaves, if not available, the Oil, of Eucalyptus 4-5 times a day for several continuous days to kill the virus in the lungs.
Here is A Review article by Mieres-Castro et al. (2021) about the "Antiviral Activities of Eucalyptus Essential Oils: Their Effectiveness as Therapeutic Targets against Human Viruses"
Australian Aboriginals are very much using Eucalyptus to Treat Infections.
5- Having plenty of Warm Drinks to wash out the virus from our body and dilute the blood to avoid blood clotting.
6- Having enough sleep and daily activities/exercises
7- Kids are proven to have High Immunity Against COVID-19, likely due to having a high amount of Melatonin, the Sleep Hormone, in their blood. So, that is why kids sleep very much as you know.
Melatonin production in our body usually decreases with increasing age. Thus, we may use daily melatonin pills after the infection based on what physicians may prescribe for us.
Here is A Review article by Carrillo-Vico et al. (2013) about the Importance of Melatonin on the Functionality of Our Immune Systems:
8- Avoid Fear/Panic as it Substantially Deteriorates the Functionality of Immune Systems against viruses and diseases.
Here is an interview by Dr. Lauren Deville about How Fear Affects Our Immune System:
In light of the ongoing challenges posed by COVID-19, it is imperative to contemplate the world's readiness to address potential future pandemics.
This discussion delves into the global preparedness, lessons learned, and strategies necessary to mitigate the impact of similar crises.
F.CHELLAI
La pandemia ha tenido un gran impacto en todo el mundo, en especial a la economía global. Muchos países han tomado medidas para tratar de disminuir el impacto económico (Programas de ayudas)
After reading an interesting article Wallace J, Goldsmith-Pinkham P, Schwartz JL. Excess Death Rates for Republican and Democratic Registered Voters in Florida and Ohio During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Intern Med. 2023;183(9):916–923. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.1154, I rethought my old results. Help me confirm/reject one of the hypotheses of my Citizen Science research. I am not a political scientist and I admit that my results may be the result of a methodological error.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, was there an opportunity to accelerate the processes of green transformation of the economy, and was this opportunity unfortunately not taken advantage of in some countries?
During the Covid-19 pandemic, due to the decline in the economic activity of companies and enterprises in many sectors of the economy, there were opportunities to accelerate the processes of green transformation of the economy, to implement the principles of sustainable economic development, to direct the development of the economy towards the green circular economy model, to achieve the goals of sustainable development, to increase the scale of pro-environmental policies, pro-environmental, pro-climate policy and thus reduce greenhouse gas emissions, reduce the level of environmental pollution, and in the situation of continuation of these processes in the coming years, it is also to increase the scale of the possibility of implementing the scenario of slowing down the progressive process of global warming, to give humanity more time to prepare for the possible subsequent negative effects of progressive climate change, the developing climate crisis. Some countries have taken advantage of these opportunities, but unfortunately only in some countries.
These issues are presented in the article:
The Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Coronavirus Pandemic on Ecological Security and the Development of International Environmental Policy
In view of the above, I address the following question to the esteemed community of scientists and researchers:
During the Covid-19 pandemic, was there an opportunity to accelerate the processes of green transformation of the economy, and was this opportunity unfortunately missed in some countries?
During the Covid-19 pandemic, was there an opportunity to accelerate the processes of green transformation of the economy?
What do you think about this topic?
What is your opinion on this issue?
Please answer,
I invite everyone to join the discussion,
Thank you very much,
Best wishes,
Dariusz Prokopowicz
The above text is entirely my own work written by me on the basis of my research.
In writing this text I did not use other sources or automatic text generation systems.
Copyright by Dariusz Prokopowicz

IS COVID-19 SIMILAR TO "H-S-V" AND OR HIV ; HERPES? WHAT ARE KNOWN ADDITIVES TO CAUSE "SKIN PEELING BY NOSTRIL." RASH NOT ABLE TO FORM. AND AWARE THAT ORANGE.COUNTY. CALIFORNIA IS ATTEMPTING TO GIVE ME H.I.V /HIV/ HIV/AIDS; /
HIV-HERPES; WHAT ARE SIGNS TO MONITOR OF EXPOSURE LEVELS ? CONCERN AS OF "4:52A.M. PACIFIC.STANDARD.TIME. #FEBRUARY25TH2024 #HATECRIMES #SKINASSAULTS #PSORIASIS #FACIALPSORIASIS #cdcgov #HATECRIMES #BEING #NATIVE #TO #CALIFORNIA #NATIVEFOUNTAINVALLEY #NATIVENEWPORTVEACHCALIFORNIA #ZIPCODEASSAULTS #FROM #USA #UNITEDSTATESOFAMERICA #92708ASSAULTS #FROM #CSULB
Been receiving emails from [email protected] to special theme issue on COVID-19 to be published this year in the official journal of the European Society of Medicine.
Just want to share that based on this article: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6625286/ , it is likely predatory journal
What is your view in relation to Lean Manufacturing impacting the recovery from COVID19? Can we blame lean for stock less production, which lead to shortages in supply chain? Or is lean going to be a critical factor in the recovery process?
The US Government Comparative Toxicogenomics database shows that Fluoride can inhibit Human immunity to viruses and pneumonia. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE), 2'-5'-Oligoadenylate Synthetase 1 (OAS1) and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM1) are included as susceptible epigenetic targets of the poison.
Wuhan is an area with high Fluoride exposure from atmospheric and groundwater pollution.
Are there more studies linking virus outbreaks or mutations with Fluoride?
For my final year dissertation, I am searching about the effect of the covid 19 pandemic on nurses' mental health.
COVID 19 pandemic has resulted in a widespread use of digital technology. In addition, it has given the boost to gig economy. Therefore, this discussion aims an interaction on how digital platforms are contributing towards freelancing.
Hi
I am working on liposome formulation. we are trying for reproduction of the size at range of +or- 20 nm. but Malvern zeta Sizer always showing different size with 2-3 peaks always.
There are number of publications just mentioned the size in number like ZXC +/- AB.
really frustrated with this first problem
and the second problem is losing hope to trust literature publications.
please share your experience, guide me if possible. help me please.
Thank you.
JR
How has COVID-19 impacted trust in the UK?
we know trust impacts health, interpersonal, organisations and even education, how has all of this changed with covid?
Covid-19 pandemic posses potent strength to invade all body cells and systems and worsening or disrupting body processes.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted the way English is taught as a foreign language?
Hello,
I am working on tourism data (tourism income and tourism arrivals) and the seasonality is very high as expected. I would like to apply Census X-13 method for the seasonality adjustment; however, all datasets have 0 (zero) value for 2020M04 and 2020M05 observations due to Covid-19 restrictions.
How can I solve this problem? Is it okay if I only put “1” for these missing values then apply Census X-13? Or do you recommend a better option?
I appreciate your help.
What are the main sources of the significant decline in economic growth and recession of the economy in 2023?
In Poland, during the SARS-CoV-2 (Covid-19) coronavirus pandemic, the government introduced a large amount of additional printed money into the economy from April 2020, which was introduced off-budget in a procedure specially created for this purpose. The central bank also participated in the procedure, buying additional new series of Treasury bonds issued by the Treasury directly. The printed money was introduced into the economy through special purpose funds created mainly in government-controlled institutions, such as the Polish Development Fund and Bank Gospodarstwa Krajowego, among others. A large amount of the printed money thus went to government-controlled state-owned companies, including, among others, the monopolistically operating large companies in the energy, fuel and mining sectors, which contribute to the leading part of the national energy industry, which produces energy mainly on the basis of dirty combustion energy, i.e. on the basis of burning fossil fuels. In Poland, still thanks to government subsidies, more than 3/4 of energy is generated from burning fossil fuels. If the subsidies provided from governments to the combustion power sector since the 1990s had fueled the development of renewable and emission-free energy, Poland would now be a modern and energy-secure country, where most of the energy would now be produced by clean renewable energy. With the aforementioned subsidies, several large nuclear power plants, many wind farms and thousands of solar installations could have been built. Unfortunately, the government preferred to be in comity with the unions operating in coal mines, lignite mines, power and fuel companies in order to support the development of combustion energy and inhibit and block the development of renewable and carbon-free energy. Thanks to the topic that hard coal is sourced from deep-sea high methane mines in the country, the government has been subsidizing coal mining for many years with many billions of zlotys. Surcharging was a permanent part of this pseudo-business, since mining had already been permanently loss-making, unprofitable for many years. In addition, thanks to the government's comity with the aforementioned trade unions, the level of wages in the loss-making fossil fuel extraction sector was high and growing despite the declining business efficiency of these companies. Since the SARS-CoV-2 (Covid-19) coronavirus pandemic, more than 300 billion in added PLN has been injected extra-budgetarily into the economy. According to some estimates compiled by scientific institutes independent of the government, this is even an amount of about 400 billion PLN. The printed money was introduced into the economy on the basis of specially introduced for this purpose regulations, covid laws, on the basis of which, on the one hand, lockdowns were introduced, temporarily excluding from real economic activity many companies, mainly service sectors. On the other hand, on the basis of covid laws introduced specifically for this purpose, printed money was transferred to the majority of companies and enterprises operating in the economy as subsidies to pay fixed costs and surcharges on salaries of employed workers on the condition that employment was maintained. Non-repayable said financial subsidies were also given to many companies and enterprises, including state-owned companies, whose business activities were not subject to lockdowns. Since in recent years the annual budget of the state is about 500 billion PLN so the estimated scale of the SARS-CoV-2 (Covid-19) coronavirus printed since the pandemic almost matches the mentioned amount. This was possible because the introduction of covid-based regulations into the economy of printed money continued until the parliamentary elections held on 15.10.2023 despite the fact that the pandemic ended much earlier. The magnitude of the negative impact on the community and on the economy quickly began to decline as early as January 2021, when a mass vaccination program was introduced on the basis of millions of coronavirus vaccines purchased by the government from several pharmaceutical companies. However, the practice of injecting printed money into the economy on the basis of covid regulations continued. The result was an increase in inflation as early as Q2. 2021. Inflation in Poland grew so fast that it was one of the highest in Europe from 2021 to 2023. With the aim of fighting inflation from October 2021, the central bank, i.e. the National Bank of Poland, rapturously began to raise interest rates. Raptly because surprising most financial analysts and economists with this action, since only two months earlier the president of the National Bank of Poland had assured during press conferences that these increases would begin in a year at the earliest. As a result, many citizens at the time took out extremely cheap long-term mortgages and business loans. Since, contrary to the banking standards of Western countries in Poland, for many years more than 90 percent of long-term loans were granted by commercial banks at variable interest rates, shifting the risk of interest rate changes to borrowers, so when the central bank raised interest rates, commercial banks quickly raised the oproc. of loans, including those previously granted, and slowly raised the oproc. of deposits and other bank investment products. Thus, the central bank's raising of interest rates had a very weak anti-inflationary effect and a fast and strong deconflationary effect. This was due to the rapidly declining creditworthiness of borrowers and falling investment levels in many sectors of the economy. For example, in the construction sector in Q3 2022, the level of investment fell by more than two-thirds on an annual basis. Because Poland's central bank raised the key benchmark interest rate from an interventionist, pandemic, anti-crisis level of 0.1 percent to 6.75 percent during the one-year period from the beginning of October 2021 to September 2022, so borrowing during the period of record, interventionist-low interest rates rapidly became more expensive. The period of the aforementioned interventionist, record-low interest rates lasted as long as a year and a half, and, according to assurances from the central bank governor, was expected to last much longer. As a result, the scale of mortgages and economic loans taken out at the time grew rapidly. When the central bank raised interest rates to a significant degree, the installments on repaid loans also increased significantly. For loans taken out at interventionist low interest rates, loan installments in the fall of 2022 were already more than double what they were at the beginning of the loan repayment. In addition, in 2022, producer inflation in some months was even more than 10 percent higher than consumer inflation. This was due to rapidly rising prices of energy and industrial raw materials, prefabricated products, semi-finished goods, wages and other production factors. Enterprises and companies, by passing on the increase in the prices of production factors to the prices of the products they sold, generated record high profits on the one hand and added to the rapidly rising inflation on the other. Commercial banks also generated record profits from mid-2021 onward as the central bank rapidly raised lending opc. rates and much slower deposit rates as interest rates rose. Despite the fact that the central bank had already stopped raising interest rates at 6.75 percent (the basic reference rate) in September 2022, the rate of economic growth was declining rapidly, the downturn was worsening and, interestingly, despite the Central Statistical Office showing no significant increase in unemployment. This happened because entrepreneurs converted full-time employment to part-time employment for many of their employees, and/or forced some of their employed staff to switch to self-employment in the setting up of sole proprietorships, i.e., establishing a sort of mini-company with which they continued to work. In this way, most of the large banks and companies have significantly improved their economic and financial situation since the pandemic, while most citizens have become poorer. For most citizens, the level of real wages, the level of savings since the pandemic has dropped significantly. Even the increase in wages in the corporate sector since Q2 2022 no longer compensated for the decline in the purchasing value of money as a result of high inflation. In addition, despite the fact that the central bank in Poland stopped relatively early, more than a year earlier than the Federal Reserve Bank and the European Central Bank to continue raising interest rates at the aforementioned level of 6.75 percent, Poland's economy went into recession in the 1st half of 2023. According to recently published data by the Central Statistical Office, Poland's recession reached 0.6 percent in April 2023. It is interesting to note that the Polish economy in 2023 experienced one of the highest downturns compared to other European Union countries, and this despite the government's continued social programs, electricity price subsidies, reduced VAT on food since the pandemic, and previously also on motor fuels (until December 2022). Despite soft fiscal policy and the government subsidy programs being developed, financed from the state's public finance system, Poland has experienced a recession. The government's energy price subsidies are due to the fact that the government was planning its re-election in the parliamentary elections, which took place in October 2023. This was one of many financial shielding instruments for citizens, which was intended to provide short-term, ad hoc some relief for citizens from rising household maintenance bills before the parliamentary elections. On the other hand, if the government's energy price subsidy system had not been in place then market energy prices would have been the highest in Poland. They would have been the highest due to the fact that Poland's energy production is extremely expensive, and mainly based on dirty combustion energy. This is a result of the government's restriction and blocking of the development of renewable and emission-free energy sources. The procedure of limiting the development of renewable energy sources and subsidizing dirty combustion energy from the system of state finances since the 1990s. While the procedure of blocking the development of renewable and emission-free energy sources, including onshore wind power since 2016 and solar power since April 2022. The result is a low level of energy security of the energy sector in Poland and some of the highest costs of energy production, not only against the background of the European Union, but also on a global scale. The lack of undertaken, necessary investments in new energy technologies, the limited scale of investments in the development of clean, renewable and emission-free energy, on the basis of which energy could now be produced in the cheapest way, is one of the key determinants limiting economic development, including the prospective development of the Polish economy. In view of the above, in recent years Poland has had an exceptionally chaotic, short-sighted pseudo-economic policy, which led, among other things, to the fact that Poland experienced a recession in Q2 2023. In April 2023, the CSO showed a 0.6 percent recession. In addition, the pseudo-economic policies pursued in recent years have resulted in a large increase in the debt of the state's public finance system. Citizens have finally noticed how irrationally the aforementioned pseudo-economic policies have been carried out in recent years, and voted overwhelmingly against the incumbent government in the parliamentary elections held on 15/10/2023. Perhaps the new government will repair all that has been destroyed in the Polish economy in recent years. Perhaps the new government will restore rationality, pro-social, pro-climate, pro-environmental, etc. in terms of its economic policies.
In view of the above, I address the following question to the esteemed community of scientists and researchers:
What are the main sources of the significant decline in economic growth and recession of the economy in 2023?
What are the main sources of the recession of the economy in 2023?
And what is your opinion about it?
What is your opinion on this issue?
Please answer,
I invite everyone to join the discussion,
Thank you very much,
Best regards,
Dariusz Prokopowicz
The above text is entirely my own work written by me on the basis of my research.
In writing this text I did not use other sources or automatic text generation systems.
Copyright by Dariusz Prokopowicz

We perceive a different form of content production on Instagram of universities since the Covid-19 pandemic to the present day. Is it a legacy of strategic communication odopted by communicators from that period?
There is a growing body of evidence to suggest that there is an association between ABO blood group and COVID-19 susceptibility and severity.
- Susceptibility: People with blood group A appear to be at a higher risk of being infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, compared to people with other blood groups. For example, a meta-analysis of 26 studies found that people with blood group A were 1.25 times more likely to be infected with SARS-CoV-2 than people with blood group O.
- More research is needed to better understand the relationship between ABO blood group and COVID-19, and to develop new strategies for preventing and treating the disease.
* tell me the susceptibility of ABO blood group effected by the covid-19?
It would have been controversial to raise questions about the Vaccination-Vitiligo link while the Pandemic was raging. Now that the Pandemic is under control, we must seek the truth.
There are plenty of articles I could locate with Google Scholar reporting incidents that suggest there is a link. For instance,
Vitiligo is recognized as an auto-immune phenomenon. Vaccinations, in general, have been associated with auto-immune reactions.
There have been two new cases of vitiligo among my acquaintances in the last two years. In both cases, the person involved had taken Covid-19 vaccinations.
A major epidemiological study is called for. The study should also cover possible associations with gender, age, ethnicity, socio-economic factors, and nutritional factors so that we will understand conditions under which a causative phenomenon is identified.
Srinivasan Ramani, 25-11-2023
In the times of COVID19 pandemic when most of the academics and research have shifted to online and distance mode, I wonder if there are postdoc positions available without the restriction of being physically present in the lab/ university. Any suggestions or links to open position advertisements can help me in grabbing a postdoc position.
White Lung Syndrome: Is it just a deteriorated immunity from infection and reinfection with COVID19? OR Is it a coinfection with COVID19 and Mycoplasma pneumoniae?
1. With clusters of cases of respiratory illnesses among children, whether the symptoms of current epidemic resemble typical mycoplasma infections?
Mycoplasma leading to pneumonia by mass infections?
2. With undiagnosed childhood pneumonia, what does it convey with symptoms having high-fever (temperatures exceeding 40 degrees C) and lung-inflammation (and continuous coughing for over a month)?
Translating from upper respiratory tract infection to pneumonia very quickly? Not a conventional Mycoplasma infection? No more a usual pathogen (and, possibly a new variant of COVID19)?
3. Do we have a clear etiology and scope of this outbreak (epidemiological and clinical information), where unusual number of children getting affected so rapidly?
4. Does white-lungs (extensive white areas in the lungs on an X-Ray – indicating widespread pathological changes in the lungs) deserve special attention now? Can Mycoplasma pneumonia cause white lung?
5. Is it just a mixed-infection (multiple pathogens getting infected @ same time; or, multiple pathogens getting infected one after another); and not a cross-infection (with other respiratory diseases)?
6. As the immune system needs to fight against upper respiratory tract infections for those kids, who get infected with Mycoplasma pneumonia, won’t the immune system will be under severe stress, when the kids also have a fever and a severe cough?
Now, what exactly (which new virus) causes another infection that could possibly invade the lower respiratory tract of the kid, and which eventually, enter the lungs?
Whether the presence of new virus, if any, keep interacting with other respiratory tracts; or, this new virus gets along well with the bacteria of mycoplasma pneumonia (which severely damages the body’s immune system) – leading to inflammatory infiltration or white lungs?
- Are you an international researcher? I am searching for some researchers who can join our projects.
- Our last project was about COVID-19 and SARS-Cov-2.
- In future projects, we are going to work on other infectious diseases and zoonotic diseases.
- If you think you have high potential in research, don't waste time and send your CV by email to me at [email protected] / [email protected].
What was the misinformation effect of conspiracy speculations during COVID-19 pandemic?
Study showed, when only 4.6% of population believed coronavirus was of a natural origin, irrational, denying and hesitant health behavior spread widely across nation.
Good day everyone,
My name is Phil- a medical student at Dalhousie University.
I'm investigating the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on presentations of asthma exacerbations to the Halifax Infirmary, and hoping to publish it to Cureus.
I'm looking for 5 folks to provide emails to potentially peer review the article- would anyone be able to help out with this please?
Thank you!
Kindly mention the types of microRNA.
I can't publish my review article on SARS-CoV-2 and I'm concerned that it may have become outdated.
Is social media use a predictor of poor academic performance? According to Pew Research (2021), “adults ages 18 to 29 say they ever use any social media sites, which is similar to the share of those ages 30 to 49.” Specifically, college-aged students self-reported using Instagram, Snapchat, and TikTok over other platforms. The majority self-reported using these services daily, often several times a day. One particular study used artificial intelligence to analyze student profiles as a predictor for success. They found students who remained engaged showed a higher predictor for continuous success, whereas at-risk students were difficult to course-correct, even with over a month remaining before their final marks. With social media use growing exponentially during and following the COVID-19 pandemic, can we correlate this growth as a predictor for student success in the classroom?
Auxier, B. Anderson, M. (2021). “Social Media Use in 2021”. Pew Research Center. Retrieved from: https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2021/04/07/social-media-use-in-2021/
Subirats L, Palacios Corral A, Pe´rez-Ruiz S, Fort S, Sacha G-M (2023) Temporal analysis of academic performance in higher education before, during and after COVID-19 confinement using artificial intelligence. PLoS ONE 18(2): e0282306. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0282306
The pandemic, COVID-19 changed the world in many ways numerous to outline. Specifically, it impacted the demographics of the healthcare industry. It also modified the scope of many businesses, globally. There are arguably long term effects of all these; evidenced by data.
Retraction "Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without a macrolide for treatment of COVID-19: a multinational registry analysis "
The retraction notice is published today, June 4, 2020.
ففي ظل الانسحاب الامريكي من منظمة الصحة العالمية وقطع التمويل عنها هل ينتهي الامر باستبدال الوكالة الدولية بكيان عالمي جديد في ظل انتقادات المنظمة من الادارة الامريكية؟ ماذا ستسرف عنه الايام في المستقبل
I will use the legend plex kit for quantification (it will be done by cytometry)
Artificial intelligence could have a significant impact on individuals, businesses, and governments. Here is what countries need to know about the benefits—and the first steps toward realizing them. The long-term potential of AI to change key aspects of the way we live and to support the operation of businesses, governments, and other organizations is hard to grasp. But even today, existing and proven AI applications can potentially create value for economies and societies around the world. Indeed, AI has contributed to improvements in quality of life for all segments of society through innovations such as predictive healthcare, adaptive education, and optimized crisis response.
The National Health Service in the United Kingdom, for instance, set up a National COVID-19 Chest Imaging Database containing a shared library of chest X-rays, CT scans, and MRI images to support the testing and development of AI technologies to treat COVID-19 and a variety of other health conditions. Businesses have seen increased productivity and operational efficiency through the use of autonomous robotics in manufacturing, AI-optimized supply chains, and intelligent cargo routing with autonomous vehicles, among other initiatives. For example, many logistics companies are using AI-powered sorting robots to optimize their warehouse operations. Governments can also harness the power of AI through personalized services and automated processes. Consider Singapore’s “Ask Jamie,” a virtual assistant that helps citizens and businesses navigate government services across roughly 70 government agencies through AI-powered chat and voice.
What was covid 19?
What impact did it have on businesses?
How can we evaluate the impact that covid 19 had on the economy
I plan to do research in this field, studying factors that explain the performance of insurance firms during the recent pandemic.
The Covid shock
Covid19 caught us by surprise. The previous comparable event had happened 100 years earlier and it had been named the Spanish flu, and it probably killed more people than World War I. The 1919 lessons learnt by health policy makers such as the US cities and European governments had been long forgotten.
Now we have learnt something
This time, it's 2023, and the Covid years, which are not over, have left a clear memory. We have no excuse, not to go prepared.
What about behavioural economists, looking at the exchange of value, time, tasks, anything, in human groups?
What can they tell us, of practical and explanatory interest for the next wave of Covid, or ahead of a similar event?
Behavioural economics scenarios and the pandemic
Can I suggest to look back at the micro-problem replicated a large number of times worldwide, where each household had to self-manage meals, schooling the children, etc. Trade-offs happened at high frequency between the members of the household, seen as agents in a behavioral nano-economy of the house...
The behavioual economist and a vademecum for the next wave?
What do you consider worthwhile for planning the next wave each household likely to have to isolate for while, at least now and then?
Let me share the assessment and model developed for the case of Covid19 "household lockdown":
REF
[1] Agent Based Model for Covid 19 Transmission: -field approach based on context of interaction, July 2020,R. Di Francesco, DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.24583.83364
[2] "Nanoeconomics of Households in Lockdown Using Agent Models during COVID-19," Sustainability, by Javier Cifuentes-Faura & Renaud Di Francesco, 2022, vol. 14(4), pages 1, February.
[3] Microeconomics of intertemporal choice in zero-space during Covid-19: a behavioral economics perspective. by Cifuentes-Faura, J., Di Francesco, R., J Health Econ 23, 559–563 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-021-01403-z
The global COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) pandemic, which was caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has resulted in a significant loss of human life around the world. The SARS-CoV-2 has caused significant problems to medical systems and healthcare facilities due to its unexpected global expansion. Despite all of the efforts, developing effective treatments, diagnostic techniques, and vaccinations for this unique virus is a top priority and takes a long time. However, the foremost step in vaccine development is to identify possible antigens for a vaccine. The traditional method was time taking, but after the breakthrough technology of reverse vaccinology (RV) was introduced in 2000, it drastically lowers the time needed to detect antigens ranging from 5–15 years to 1–2 years. The different RV tools work based on machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI). Models based on AI and ML have shown promising solutions in accelerating the discovery and optimization of new antivirals or effective vaccine candidates. In the present scenario, AI has been extensively used for drug and vaccine research against SARS-COV-2 therapy discovery. This is more useful for the identification of potential existing drugs with inhibitory human coronavirus by using different datasets. The AI tools and computational approaches have led to speedy research and the development of a vaccine to fight against the coronavirus. Therefore, this paper suggests the role of artificial intelligence in the field of clinical trials of vaccines and clinical practices using different tools.
Source:
How do I share a public link of my paper in the network?
I got the journal permission to share the following link of my recent paper
How do I share it technically?
Sincerely
Abira
I want to build a phylogenetic tree of data of sequencing of dengue, but I don't have experience in that, I had had the experience in SARS-CoV-2, in that case I used my sequences (query), the sequence more related to my query (using Audacity Instant in GISAID) and the references sequences, all these were my dataset (for SARS-CoV-2), but for dengue is there a program similar to Audacity instant? Any recommendation?
Thanks for any opinion.
Is it not lowering the quality of education? What has been the purpose of exam invigilation over the years before the COVID-19 pandemic? Will their degrees be authentic? Will they not be half-baked? Is it not an online copy-paste game? What do you think?
HRM practices have been hugely affected by the pandemic across the globe. Is there any possibility of a change in the practices in the expected POST-COVID-19 era? Are we going to resort to our old and/ traditional HRM practices? What is your take on this as a practitioner or academic? Kindly share your thoughts with us, thank you.
My study is on the events of the historical change to HRM practices during and post COVID-19 respective organizations
Is the Omicron soup causing the WHO's Greek naming scheme to fail?
The World Health Organization is investigating a new COVID variant called “Arcturus,” which is likely causing a new surge of cases in at least 34 countries. The subvariant of Omicron, XBB.1.16, has been named “Arcturus” by SARS-CoV-2 variant trackers and is very similar to the U.S. dominant “Kraken” XBB.1.5, which is the most transmissible COVID variant yet, according to Dr. Maria Van Kerkhove, WHO's COVID-19 Technical Lead, at a news conference on March 29, 2023.
Arguably, the omnipresent Omicron may have thrown the WHO's COVID-19 variant naming system into disarray. Omicron's rapid growth has made it increasingly difficult for ordinary people to keep up with the dizzying array of subvariants it has created. The WHO originally intended to simplify public communications by assigning Greek letters to variants it deemed threatening. For example, the WHO classified “Kraken” XBB.1.5 and “Arcturus” XBB.1.16 as Variants of Interest (VOIs) on January 11 and April 17 of this year, respectively. However, because “Kraken”, “Arcturus”, and "Centaurus" (BA.2.75, a Variants Under Monitoring (VUM)) are Latinized words, they would cause the WHO's Greek naming scheme per se to fall apart.
References:
- World Health Organization. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants. https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants
- World Health Organization. WHO announces simple, easy-to-say labels for SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Interest and Concern. https://www.who.int/news/item/31-05-2021-who-announces-simple-easy-to-say-labels-for-sars-cov-2-variants-of-interest-and-concern
I'm expecting to use stock prices from the pre-covid period up to now to build a model for stock price prediction. I doubt regarding the periods I should include for my training and test set. Do I need to consider the pre-covid period as my training set and the current covid period as my test set? or should I include the pre-covid period and a part of the current period for my training set and the rest of the current period as my test set?
In one work, suppose multi-disease (skin cancer, covid-19, Monkeypox, and lung disease) data analysis and disease prediction, I used 5 ML models (KNN, GB, RF, SVM, and Ada boost) after pre-processing steps (data cleaning, encoding, missing value handling, outliers handling, feature engineering, etc.) now while analyzing the model performances I want to use statistical test on our ML models. I found no previous works that work on the same kind of dataset instead most of them worked on similar types of disease (i.e. Lung cancer (3 types) = 11, 12, 13) detection. I want to know, (1) How can I compare my work outcomes with others as they not using similar data? (2) When applying the statistical test will be appropriate? (3) Why should I use it? (4) How can I perform statistical tests for my work?
There is an abundance of new scientific literature that has been published (over the past year and a half) on new clinical research developments of electronic-nose (e-nose), or artificial olfaction and related technologies, for the early detection and diagnosis of Covid-19 coronavirus infections in human patients. This question centers around the idea of whether any of these research approaches have actually been further developed (beyond proof of concept) to the extent that new diagnostic methods (based on e-nose instruments) are already being used in clinical practice. I am not looking for literature (published research) on experimental trials, but rather actual examples of clinical uses (locations of medical facilities and technologies used) that have already been implemented in a known clinical setting or for point-of-care testing (POCT).
To date, the human cost of coronavirus (COVID-19) is more than 13 000000 infections, and more than 570000 death worldwide. The economic cost so far has been staggering. Many economies almost come to a halt. The impact on supply, demand, the financial market is affecting both larger and smaller firms. However, SMEs are at a disadvantage due to limited resources, existing obstacles in securing capital, and the span of time over which they can survive this pandemic compared to the larger firms.
How SMEs and new start-ups are going to handle this pandemic? Can they survive it or a great majority of them will go out of business? Should the government step in to help?
Since the start of the COVID-19 Pandemic, many governments and private organizations allocated large sums of money to fund projects dealing with various areas related to this virus. The vaccine is the most prominent area but detection, caring and monitoring of the patients revealed that the current medical equipment is not adequate and sufficient. Are these funding going to lead to invention or innovation? have you seen any report of innovation in medical technology in your community?
Economics of different countries is collapsed because of COVID-19. What you think? What will be the opportunities of funding at higher studies after this Pandemic? Please share your thoughts regarding this issue. Your valuable thoughts will be highly appreciated.
What kinds of problems did healthcare workers experience using protective equipment during the COVID-19 outbreak?
What kind of problems did the healthcare professionals experience regarding the supply of materials during the treatment and care of the patient during the covid-19 outbreak?
Have nurses used innovative practices in care? Could you share the innovation examples in nursing used in this process?
During the COVID-19 epidemic, nurses working in a hospital setting may be physically, mentally, socially, ethically, etc. what kind of problems does he have?
We need your scientific research and help with the answers to these questions in order to share them with healthcare nurses.
Hi all,
Can you tell us how COVID 19 has triggered most of the innovative processes in the public and private sectors during this period of uncertainty? and from the non-profit sector? in your country?
- Are you an international researcher? I am searching for some researchers who can join our projects.
- Our last project was about COVID-19 and SARS-Cov-2.
- In future projects, we are going to work on other infectious diseases and zoonotic diseases.
- If you think you have high potential in research, don't waste time and send your CV by email to me at [email protected].
If not approved then how we have come to know approved for working of covid 19 patients or by research through research journals.
If trial details of recovered patients after application? Is it like antiviral vaccines or antibiotic. Is it possible to working like Ramdesiver blood clotting.
This RG open question is linked to the previous about the dramatic evolution (partly unexplainable) of COVID19 in Northern Italy during wave 1.
The previous RG open question is reported below🔴 and resulted in a completely alternative model for the evolution🟨 of SARS-CoV/2 from pre-pandemic phase to pandemic phase.
In this specific RG question, the intention is to create an open discussion on the possible emergence of a violent outbreak of avian flu or similar in central Europe.
This concern arises from a qualitative model that links three events which in the past have always characterized the violent explosion of a bird flu or similar.
The model involves three steps.. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/367046404
---Coronavirus Epidemic/Pandemic;
---Conflict/War partly out of control;
---Pandemic avian flu or similar.
The ABSTRACT of the model can be consulted directly here.. https://www.researchgate.net/figure/46_fig2_367046404
This RG open question will serve to accumulate data both for and against this dire possibility.
Thanks to all the participants.
|--sv--|
🔴The novel Coronavirus in N. Italy, Lombardia 【 COVID19 / 2019nCoV / SARSCoV2 】 shows a fatality rate compatible with SARS-MERS. Why?? MAR.2020. -- https://www.researchgate.net/post/The-novel-Coronavirus-in-N-Italy-Lombardia-COVID19-2019nCoV-SARSCoV2-shows-a-fatality-rate-compatible-with-SARS-MERS-Why
🟨Link between the start of pandemic SARS-CoV/2 (COVID19) and the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan (Hubei: China): the furin cleavage site of spike protein. FEB.2022. -- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358443761

My research paper aims to address three key research questions that focus on exploring the specific legal implications of COVID-19 on the international sale of goods and understanding how international trade laws and agreements have adapted to the challenges brought about by the pandemic.
1. What are the specific legal implications of COVID-19 on the international sale of goods?
2. How have international trade laws and agreements adapted to the challenges posed by the pandemic?
3. What are the implications for contract formation, performance, and remedies in international sales contracts due to COVID-19?
"Cardiac MRI is the most important noninvasive imaging modality for evaluation of myocarditis"
The size of the protein is 154KDa his-tagged. I have tried inducing with 0.5mM IPTG for 4hrs at 37 degrees. I have tried different strains BL21-De3 Gene X, shuffle T7, and artic but still no expression. I have also tried 25 degrees overnight. Any suggestions might be helpful.
Hello all, appreciate your help as it is much needed. I am trying to understand whether my thesis should be a research paper or a case study. I want to study the effects of disruptive events of global supply chains and then focus on the retrospective of one company. Is this automatically a case study, or can I follow the structure of a research with literature review on the overall problem and then focus on interviewing points of contact of said company to gather my findings and propose a management model to help the company respond to disruption in the supply chain?
Thank you
In recent years, number of vaccine have been approved to fight against Covid-19, list of approved is available at FDA site. We are looking for sequence of these vaccine (RNA sequence in case of mRNA vaccines and amino acid sequence in case of protein based vaccines. I will highly appreciate help of community in searching sequence of vaccines.
Why does the Omicron VOC of SARS-CoV-2 not damage people's lungs as much as the Delta?
Dear Researchers,
The COVID -19 pandemic caused by SARS CoV-2 is taking away many lives. Till now there is no approved vaccine to tackle this. Literatures and media are giving us information that it will take around 6 to 8 months more to get the vaccine. Besides, alternative medicines are getting attention to treat COVID-19. Will plant metabolites be the hope to get the therapeutics before other drugs or vaccines. How it is possible? Share your thinking, please.
I published a short article back in 2021 in Academia Letters, titled ˝Can a Multi-Epitope Vaccine be a solution for COVID-19 pandemic˝?
Here is the abstract:
Problems associated with Wuhan spike protein-based vaccines are the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 strains that are more or less resistant to Wuhan spike protein-based vaccine-induced immunity, and toxicity of the spike protein (S protein alone can damage vascular endothelial cells). Multi-epitope vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, excluding the spike protein, could potentially be less toxic than Wuhan spike protein-based vaccines with less serious side effects, but still enough immunogenic to elicit protective immune response. Another potential benefit of a multi-epitope COVID-19 vaccine is that, taking into account the fact that most of the new SARS-CoV-2 strains carry significant new mutations in the spike protein and less significant mutations in other structural proteins of the virus, it could provide more potent immune response against new SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Link:
And now it is happening! I am so excited!
Researchers (Arieta et al) created a new multi-epitope vaccine.
Here is the abstract:
T-cell responses play an important role in protection against beta-coronavirus infections, including SARS-CoV-2, where they associate with decreased COVID-19 disease severity and duration. To enhance T-cell immunity across epitopes infrequently altered in SARS-CoV-2 variants, we designed BNT162b4, an mRNA vaccine component which is intended to be combined with BNT162b2, the spike-protein-encoding vaccine. BNT162b4 encodes variant-conserved, immunogenic segments of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid, membrane, and ORF1ab proteins, targeting diverse HLA alleles. BNT162b4 elicits polyfunctional CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses from diverse epitopes in animal models, alone or when co-administered with BNT162b2 while preserving spike-specific immunity. Importantly, we demonstrate that BNT162b4 protects hamsters from severe disease and reduces viral titers following challenge with viral variants. These data suggest that a combination of BNT162b2 and BNT162b4 could reduce COVID-19 disease severity and duration caused by circulating or future variants. BNT162b4 is currently being clinically evaluated in combination with the BA.4/BA.5 Omicron-updated bivalent BNT162b2 (NCT05541861).
Link:
Let me know what do you think!
As you are aware after getting a COVID-19 vaccine side effects can vary from person to person. some are having immediate effects which are expected and some are facing it till date.
Please write if u still face any such after 2 years of time.
Education is fundamental in society, and COVID-19 had a great impact on it. Online education has become essential for many students and teachers necessary to offer a quality education.
Did the Covid 19 pandemic put the theory of international relations in a crisis of interpretation, or did it put it in front of the criteria of justification? Was Concy Wright right in his words about the total theory in international relations?
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a pandemic on March 11, 2020, and announced the END of public health emergency of international concern on May 5, 2023. However, Covid-19 continues to spread, and the virus is evolving and remains a global health threat with continued vulnerabilities in our communities.
Get a chance to win one of four 50$ gift cards by answering this 5 minute survey. It's part of a project titled ‘Vaccine Community Innovation Challenge’ guided by the Public Health Agency of Canada, in order to increase COVID-19 booster shot awareness. Prize winners will be announced at the end of the campaign.
The questions are general; answers are confidential and used for statistical analysis only.
Click here to start the survey: https://lnkd.in/esZyWF4N
Moderna claims that detection of Covid19 Anti-Spike IgG antibody found in the lungs of Rhesus Macaques (that have high natural immunity against the virus) was evidence that the Spike Protein antibodies resulting from jabs in the arm circulated in Blood and somehow penetrated the Blood-Lung Barrier.
However there is an interesting paper from very early in 2019 that shows Anti-Spike IgG causes Severe Acute Lung Injury by skewing macrophage responses.
A doctor named Joseph Lee has challenged Dr Fauci, the editor of New England Journal of Medicine and many other scientists, plus the mRNA jab manufacturers to prove that the insides of lungs are protected by their LNP delivered materials.
He reports that they don't give satisfactory replies to his questions about the Blood Lung Barrier and has offered a reward for any proof via Twitter.
His website carries useful details.
Could Alveolar Macrophages be a conduit for antibodies?
How long is going to take for IgM antibodies to fade following vaccination against COVID-19
Cognitive impairment following COVID-19 is described in the research literature. Is there evidence for therapy to address deficits for long COVID?
This year is known as the "Black swan of 2020" and created a mystifying situation before entrepreneurs. Now entrepreneurs should take it as an opportunity to start new ventures and rethink and restrategize to fight back. I am interested to know about your views specifically tourism, Banking, food and beverages, and education sectors.
The Covid-19 pandemic is coming to an end around the world and now is the time to analyze its impact on all institutions of society one of the most interesting to study in our opinion is education. A large number of researchers note that during the quarantine restrictions and online learning, the process of incorrect borrowing and violation of the principles of academic integrity has increased significantly. Also at the end of 2022, neural networks based on artificial intelligence received wide publicity and application, which also raises many questions in the field of maintaining academic integrity.
We would love to hear your thoughts and recommendations on maintaining the principles of academic integrity in the student community in 2023.
Regarding your personal experience with COVID-19
I recently read you thesis, The Concept of the Ascent of Prayer by Sixteenth-century
Jerusalem Kabbalist, R. Joseph ibn Zayyah. Question: Does Zayyah discuss in his Perush le-Tefilah the meaning of the six Mahs [Who are we? What is our Life, etc] in the prayer Ribbon Ha'Olamim located before the first Shema? Are you familiar with additional explanations of the six Mahs?
Unfortunately, due to the Covid-19 pandemic libraries are closed and I cannot travel due to recent cardiac surgery and my age. Any assistance would be appreciated.
Thank you.
Michael Alter
Dear colleagues kindly help me out
What child social development support programmes, child psychological support programmes are being developed in relation to the increasing scale of psychological problems in children, which have significantly worsened since March 2020, i.e. since the lockdowns, national quarantines, universal e-learning, social distancing in public places, etc., introduced during the coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic?
At the beginning of May 2023, the World Health Organisation lifted the state of global epidemiological emergency associated with Covid-19. In Poland, the state of heightened epidemiological emergency associated with Covid-19 is not due to be lifted until the end of June 2023. This is likely to increase the scale of ongoing research into the various secondary effects of the Covid-19 pandemic, both the post-pandemic, post-vaccine health effects, then also the social and economic effects, including, for example, on the issue of rising inflation from 2021 generated by the introduction of a large amount of additional money into the economy during the Covid-19 pandemic, which was mainly intended to limit the scale of the increase in unemployment caused by the introduced lockdowns. In Poland, the PIS government is mainly responsible for the deterioration of children's mental state, which unreflectively and without applied research and public consultation introduced large-scale lockdowns imposed on selected sectors of the economy, national quarantines, universal e-learning, social distancing in public places, etc. ... and even a ban on entering forests during part of the period of wave 1 of the pandemic.
From mid-2022 onwards, more and more comparative studies began to appear, which compared internationally the question of the correlation between the rate of development of the pandemic, the number of deaths categorised as caused by the severe Covid-19 disease state and the occurrence of co-morbidities, usually in more than 90 per cent of cases, and the so-called 'anti-pandemic safety instruments' introduced to varying degrees in individual countries. The results of the study did not confirm the findings of the study, which was based on the results of the research carried out by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The results of the research carried out did not support the thesis regarding the validity of the
of the lockdowns introduced during the coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic as an instrument to significantly reduce the level of mortality caused solely by the severe Covid-19 condition, exclusively, i.e. by subtracting the factor of co-morbidities. In some countries, the generating factors of specific comorbidities were key influential determinants shaping mortality levels. For example, in Poland, where, due to the government's neglect and deliberate slowing down and blocking of the development of renewable energy sources in recent years, more than three quarters of energy is still produced by the technologically backward dirty power industry based on burning hard coal and lignite, which generates the worst air quality in cities during heating periods compared to Europe and the world. This poor air quality, determined by high levels of particulate matter (PM 2.5, PM 10, etc.), is the source of premature deaths, estimated at around 50 000 people, i.e. deaths caused by respiratory and other diseases resulting from high levels of air pollution. Such diseases are examples of diseases coexisting with Covid-19, which were compounding factors in the level of mortality qualified as caused by these diseases in combination with Covid-19 during the pandemic. In the government-led pandemic risk management process, different structures were adopted to prioritise safety on the one hand for health and on the other hand also for socio-economic safety. Different solutions were adopted in the countries in terms of the applied anti-pandemic safety and anti-crisis instruments with regard to the economy. Consequently, the effects of these measures were also not the same. The economic impact of the coronavirus pandemic (Covid-19) and the applied anti-pandemic instruments also varied significantly between the various different industries and sectors of the economy.
These systemic anti-pandemic measures mainly benefited the technology sectors, companies operating on the Internet, businesses developing e-commerce, courier companies, state-owned companies receiving additional government contracts for the production of anti-pandemic assortments, e.g. hand disinfectant fluids, production of protective masks, etc. On the other hand, there were many more companies and enterprises, mainly operating in the service sectors, which were subject to lockdowns and suffered severe financial losses, some going out of business because of them, which in macroeconomic terms generated a deep recession of the economy during the 1st wave of the pandemic. However, as it later turned out, there were many more problems caused by such anti-pandemic socio-economic policies. Among these various secondary effects of the negative and particularly socially significant problems generated by the misguided antipandemic socio-economic policy, one stands out the increasing scale of psychological problems in children, which have significantly worsened since March 2020, i.e. since the lockdowns introduced during the coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic, national quarantines, universal e-learning, social distancing in public places, etc., and have been exacerbated by the controversial pseudo-reforms applied to the education system over the past few years. In Poland, this problem is very serious. This is confirmed, inter alia, by the data on the growing scale of child suicides in the period from 2020 to 2022. Lockdowns, national quarantines, universal e-learning, social distancing in public places, etc., introduced and applied on a large scale during the coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic in Poland, have caused disorders in the social development of children and adolescents. In view of this, it is essential to create and develop programmes to support the social development of children, programmes of psychological assistance for children, which should prevent the growing scale of psychological problems in children.
In view of the above, I address the following question to the Honourable Community of scientists and researchers:
What programmes of support for children's social development, programmes of psychological assistance for children are being developed in connection with the increasing scale of problems of a psychological nature in children, which have significantly worsened since March 2020, i.e. since the lockdowns introduced during the coronavirus pandemic (Covid-19), national quarantines, universal e-learning, social distancing in public places, etc.?
What child development support programmes, child welfare programmes are being developed in relation to the increasing scale of mental health problems in children?
And what is your opinion on this topic?
What is your opinion on this subject?
Please respond,
I invite you all to discuss,
Thank you very much,
Best wishes,
Dariusz Prokopowicz

For a research on a psychotherapeutic intervention for health care employees in the face of COVID-19 I am looking for the Nursing Stress Scale or a similar instrument to measure stress in nursing-staff. It would be great if anyone could help me.
Thank you :)
Regarding to the question (covid-19 is a natural virus or created by human) who we can realize the fact of this issue?
(PDF) Correlation of COVID-19 US Map and US Geoelectric field Map. First impression, Facts, and Hypotheses (researchgate.net)
EPO levels were significantly lower in critical and deceased Covid-19 patients:
Suggested treatment for both Covid-19 and LongCovid: rhEPO :
Signs, symptoms and co-morbidities in PostCovid indicate continued EPO deficiency:
Pathogenesis : the immune response to the virus is so strong (with inflammatory cytokines), that it damages the kidneys EPO production.
Inflammatory cytokines
TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, IL1B, IL6, IL17A ... (etc.) all suppress EPO:
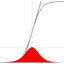
Figure 1:
arrow direction = "increase of") EPO treatment would move "Covid-19" to the right in the figure. It follows that too much EPO can be harmful - at the far right in the figure.
There could be further causes of EPO deficiency:
Obesity, diabetes and pain in the joints
Muscle pain, exercise intolerance, lack of energy and mitochondria
Lack of energy - red blood cells
EPO regulates the lives and deaths of red blood cells.
The primary effect of EPO is increased number of red blood cells and thereby increased oxygen uptake, which is much needed in severe cases of Covid-19 - and in LongCovid.
Article Anemia of inflammation
EPO is the natural inhibitor of the Sphingomyelinase-Ceramide-Pathway :
(Hemoglobin is measured in gram per liter or deciliter blood. It says nothing about blood volume, how many liter of blood the patient has. There is a reason for, that most LongCovid patients look pale).
HDL-Cholesterol deficiency, lipids and thrombosis
EPO inhibits (/regulates) NF-kappaB and thereby reduce TNF-alpha:
Co-aministration of thrombolytic therapy and rhEPO should be avoided:
Complement system and Micro-amyloid-fibrinogen-clots
EPO regulates the Complement system:
The micro amyloid fibrinogen clots are yet another sign of erythropoietin deficiency in LongCovid :
(press DOI link to see full text)
And EPO treatment is how to get rid of them :
Decreased platelet activation through glycoprotein VI
Article TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor-α)
Endothelial dysfunction and heart disease
Hypocortisolemia
... caused by EPO-deficiency, inflammatory stress and maybe corticosteroid treatment.
Erythropoietin negatively regulates pituitary ACTH secretion :
"Prolonged or exaggerated stress response may perpetuate cortisol dysfunction, widespread inflammation, and pain." :
Hair Loss
Brain fog and demyelinaton
As mentioned above ("Lack og energy - red bloodcells") is EPO essential for sphingomyelin, and the same goes for myelin:
Erythropoietin re-wires cognition-associated transcriptional networks:
Introducing the brain erythropoietin circle to explain adaptive brain hardware upgrade and improved performance :
Microglia activation and neuroinflammation
Brain erythropoietin fine-tunes a counterbalance between neurodifferentiation and microglia in the adult hippocampus:
Article The neurobiology of long COVID
An effective erythropoietin dose regimen protects against severe nerve injury-induced pathophysiological changes with improved neural gene expression and enhances functional recovery:
EPO prevents neuroinflammation and relieves depression via JAK/STAT signaling :
Depression and other mental disorders
Cognitive impairment in children
EPO is essential for brain development:
Blood-brain-barrier
Blood–brain barrier disruption and sustained systemic inflammation in individuals with long COVID-associated cognitive impairment:
The relationship between erythropoietin pretreatment with blood–brain barrier and lipid peroxidation after ischemia/reperfusion in rats
Erythropoietin protects against hemorrhagic blood–brain barrier disruption through the effects of aquaporin-4
Loss of or distorted taste
EPO is vital for the maintenance of both myelin and sphingomyelin.
Blindness
Inhibiting Ceramide synthesis preserves photoreceptor viability and functionality :
Hearing loss
EPO ↔ Melatonin ↔ Serotonin ↔ EPO --> dopamine
and insomnia
(they mutually increase one another)
Fatty liver
Alcohol intolerance
Kidney damage
Recombinant human erythropoietin reduces rhabdomyolysis-induced acute renal failure in rats
Erythropoietin protects against rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury by modulating macrophage polarization
Inflammation and lung tissue damage
(Not meaning that inflammation is only in lungs)
Autoimmunity
CD8+ T cells and activation of T-cell receptor heterodimers
”NIH-funded study suggests need to boost CD8+ T cell response after infection.”:
Article STAT5 and CD4+ T Cell Immunity
Mitochondrial dysfunction, viral persistence and deficient phagocytosis
With "exhausted" CD8+ T cells, it is worth remembering that immune cells also have mitochondria, and they need energy to do their job:
SARS-CoV-2 fragments may cause problems after infection:
Correction of Deficient Phagocytosis During Erythropoietin Treatment in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients:
Gut microbiota dysbiosis
Iron dysregulation
Iron dysregulation and inflammatory stress erythropoiesis associates with long-term outcome of COVID-19:
Dysautonomia and POTS
The causes of these conditions are not fully known/understood/agreed upon. But many very likely explanatory factors have been mentioned in the above.
Erythropoietin in Autonomic Failure:
"These patients also have a significant reduction in plasma erythropoietin":
Sexual and reproductive function
Men
Endothelial Dysfunction in Erectile Dysfunction:
In male patients sexual desire, frequency of sexual intercourse was strengthened after rhEPO therapy:
Women
Improvement of sexual function was remarkable in female patients:
Why women more often suffer from LongCovid ?
Adult females mount stronger innate and adaptive immune responses than males: https://www.nature.com/articles/nri.2016.90
This means a stronger EPO-TNFalpha imbalance.
Estrogen suppresses and testosterone increases the production of EPO in the kidneys:
This makes a threshold for younger to middle age female patients to recover their own EPO-production, while in particular younger men quickly recover from or don't get Covid-19 and rarely suffer from LongCovid.
Insights into early recovery from Long COVID—results from the German DigiHero Cohort:
This may thus also explain the age-distribution in LongCovid.
Racial/ethnic differences
Conclusion
EPO deficiency is "the common denominator" in both LongCovid and in Covid-19.
Covid-19 and LongCovid are immunologic, hematologic, metabolic, neurologic and endocrinologic diseases.
That sounds complicated, but it is all due to deficiency of a single substance, that stands ready in our common medicine cabinet.
Dear colleauges. Greetings. Is it possible that after having alteration of amino acid in Covid-19 , we got a new clade?
I am conducting qualitative research on teachers' perceptions about the impact of covid-19 pandemic on their performance.
How do draft the survey questionnaires to collect the data.
I need help with the sampling questions.
Thank you.
Due to this pandemic severe crisis occurred throughout the world. Human hunger indexed has been increased due to this pandemic.
I am doing qualitative studies; can anyone help me with how to draft a questionnaire to collect information about the impact of covid-19 on teachers' performance.
I am pleased to share that our paper entitled “Did Outside Directors’ Firm-specific Accumulated Knowledge Benefit the Firm’s Stock Performance during COVID-19?” has just been accepted for publication in Australian Journal of Management!
I co-authored this paper with Dr Dharmendra Naidu from Monash University in Australia.
Our research contributes to “the role of corporate governance in enhancing firm performance during a crisis…Our research is the first to show how prior social interactions between outside directors and inside directors over their tenure positively contributed to firm performance during COVID-19 crisis. We contribute by advocating on the relevance of outside directors’ accumulated knowledge about the firm to decision making during COVID-19 crisis.”
We add to the prior literature “by examining the effect of outside directors’ internal social capital on their utilization of firm-specific human capital during the COVID-19 collapse period.”
“Our results suggest that outside directors’ board tenure around 10 to 13 years was optimal during the COVID-19 collapse period. Our results are also relevant to regulators and stakeholders of firms in the Asia-Pacific region including Australia because recent studies using Australian firms show that their average board tenure is around 6 years”, (Naidu and Ranjeeni, 2023).
#Research #OutsideDirectors #AccumulatedKnowledge #BoardTenure #FirmPerformance #StockPerformance #CapitalMarkets #COVID19 #HumanCapital #InternalSocialCapital #AustralianJournalofManagement #AJM #Publication
Post COVID-19 environment will be unbearable. Under this scenario, we must explore & exploit the embedded & dormant opportunities as well as resources to the greater extent possible without jeopardizing the mother Earth.
I’ve planned and organized over 87 international academic conferences and workshops during my 25+ years of experience as a professional conference organizer. During this time, I’ve learned the crucial steps of planning and managing the submission process for abstracts and full papers.
I am writing this blog post at the suggestion of academicians who are members of a scientific committee organizing their 35th international academic conference. They were unaware of the current state of conference management software and how easily it can manage the scientific part of an academic conference, eliminating most gaps through the automated process. They were spending valuable time and effort to create error-free conference programs and books of abstracts.
I apologize for the length of this article and for taking up your time. I’ll dive into the details as suggested by the scientific committee’s academicians.
Before diving in, I want to take a moment to inform you that we have developed Meetinghand Abstract Submission Management Solution to address most challenges facing academic conference planners. So, if you wish to learn more about Meetinghand, please contact with us..
Before setting up the conference submission form and starting to collect abstracts, I always consider the following issues;
- How to encourage authors to submit their works easily?
- How to manage the evaluation process easily?
- How to notify authors?
- How to keep the abstracts updated from start to finish?
- How to add the abstracts to the conference agenda easily?
- How to prepare an error-free book of abstracts and keep it up to date?
- As well as, how to check the authors' registration status?
I will try to proceed through questions in a manner similar to "five Ws and one H" for a better convey of the important points and not clash with the inquisitive nature of academic readers.
Please keep in mind that I will approach the subject from a broader perspective using the term “conference” to include most types of academic events such as congresses, workshops, seminars, symposia, and training courses.
You can create your custom checklist to suit your exact needs, and even email me for help or suggestions, as each event may be unique.
As a general rule, I always consider;
- The next step, without forgetting that our end goal is always to go forward, without getting lost in the maze.
- What encourages authors to submit their works?
- How can authors submit their papers more easily?
Here are the questions that I bring to the table of the scientific committee and the conference organizers, as well as my suggestions.
What are the main objectives and considerations for organizing a conference and managing its scientific framework?
What are the main objectives you aim to achieve for the conference?
Various goals can be pursued, such as creating a scientifically high-quality conference program, gathering numerous abstracts, attracting a high number of participants, collecting full papers, and publishing proceedings.
However, achieving all these goals may not be easy. Therefore, it’s crucial to clarify the most important (final) goal of collecting abstracts, as it will shape the approach moving forward.
Are you planning to publish conference proceedings?
Some conferences publish proceedings in formats such as conference books, special journal issues, books of full papers, or extended abstracts. Publishing conference proceedings is recommended if previous conferences have done so, as attendees might expect it. However, this requires significant effort and in-depth review and may include detailed methodologies, analysis, results, and discussion of the presented research. If it is necessary, consider publishing it as a special issue of a scientific journal through a win-win partnership, as they usually have greater experience in this field.
What information will you include in the call for abstracts?
It is recommended to keep the email announcement message concise, containing only a brief overview of the conference theme, a link to the conference webpage, social and academic benefits of attending, logos of organizer and supporter institutions, and using friendly language.
On the conference webpage, expand the information by adding important dates, scientific topics, presentation types, submission, evaluation, and notification processes clearly, and a brief note about the abstract format, such as word limits.
Will you ask the invited speakers to submit an abstract?
It is suggested to gather abstracts from invited speakers and include them in the book of abstracts to increase their perceived value. Invited speakers play a key role in attracting attendees, enhancing visibility, and increasing the conference’s impact.
What deadlines should you set for abstract submission?
When determining the abstract submission deadlines, consider the conference dates, the time required for authors to prepare their abstracts, and the time needed to create and announce the conference program.
Generally, conference planners declare the following deadlines:
- Abstract submission start date,
- Abstract submission deadline,
- Evaluation results announcement date,
- Author registration and payment deadline.
It's important to note that organizers may have a tendency to prolong the deadlines as participants often anticipate it. Allowing a longer submission period for poster presentations can be beneficial since they are generally easier to manage and schedule within the conference program.
What presentation types should you consider?
Oral and poster presentations are the basic presentation types. Workshops, panel sessions, roundtable discussions, and research forums are some of the popular types. However, virtual presentations gained popularity during the COVID-19 pandemic due to their cost-saving advantages.
Dr. Arber suggests including PechaKucha as a presentation format, bridging the gap between traditional poster and oral presentation formats. This format likely appeals to younger generations and early career researchers, as it aligns with modern technology and fast-paced communication styles.
Additionally, offering a "Poster, if not Oral" option provides flexibility when constructing the conference agenda and helps satisfy authors’ preferences.
How many abstracts should each author be allowed to submit?
Assessing the conference program to determine how many presentation slots are available and how many abstracts have been received at previous conferences is important to define the submission limits for each participant.
Conference planners commonly accept more abstracts than available slots for various reasons, such as:
- Approximately 25% of the accepted abstracts may not pay the registration fee or might withdraw later due to different reasons. The deadline for author payments is crucial in this regard.
- Adding parallel rooms or reducing the oral presentation time from 20 minutes to 15 minutes can result in a 25% increase in presentation capacity.
But no need to worry. Because usually many creative and practical solutions will emerge to address the issue of having more submissions and participants than anticipated.
How to build and structure an abstract form? Step-by-step checklist
Should you collect abstracts in a single format?
Considering the scientific scope of the conference and the potential attendees, it is important to ensure the abstract submission format and requirements match the expertise level of the participants. It may be necessary to collect submissions in different formats and provide scientific abstract examples. However, if the conference and attendees are not dealing with specialized technical or niche subjects, it is highly recommended to use a single abstract format and keep it as simple as possible.
Will you collect the abstracts in text or file format?
It is generally recommended to gather abstracts in text format and full papers in file formats. Collecting abstracts as text can save time and effort by enabling an automated process for:
- Styling the content, such as font type, font size, and the use of uppercase or lowercase letters.
- Applying required submission rules, such as word limits, title length, affiliations, and keywords.
- Allowing authors to make necessary updates.
- Helping organizers and reviewers track the abstract updates and versions easily.
- Keeping the conference agenda updated.
- Simplifying the abstract submission process for authors.
- Exporting abstracts and content of the book of abstracts error-free.
- Avoiding common mistakes made by authors.
- Standardizing the appearance of abstracts with formatting rules.
- Making the review process easier and more effective.
- Implementing a 'what you see is what you get' approach for authors, reviewers, and organizers.
- Notifying authors personally and delivering acceptance letters and documents.
To emphasize the importance of the abstract submission format, consider this analogy: Collecting abstracts as text (instead of files) is similar to using an abstract management platform (instead of email), which significantly reduces manual work and errors.
Should you provide a guideline for abstract formatting?
Providing authors with a concise guideline will inform them about the appearance and content of the abstract, including aspects like scope, methodology, and length.
However, it is often unnecessary to provide an abstract template for the abstract format, as abstract submission forms not only guide and demonstrate the expected format but also ensure that authors meet the abstract requirements.
Do you require submitters to select scientific topics of the conference?
Asking authors to choose a relevant scientific topic can help organizers efficiently assign each submission to the appropriate reviewer and session in the conference program. Additionally, setting up an "other" topic option can help you in identifying abstracts that may not align with the scope of the scientific conference, offering insights into potential subjects for future conferences.
What information should be requested from the authors in the abstract submission form?
The abstract submission form is an online tool used by conference organizers to collect abstracts from potential presenters or participants. It is essential to keep the abstract submission form simple and straightforward, focusing on collecting the required information and formatting the abstract correctly.
Key pieces of information to request include:
- The scientific topic related to the abstract,
- The preferred presentation type (e.g., oral, poster, PechaKucha, poster if not oral, etc.),
- The abstract title,
- The authors of the abstract, including their affiliations, presenter and corresponding authors, and author order,
- The abstract content, including minimum and maximum word limits, options for adding figures and tables, and other relevant details,
- Keywords describing the abstract content,
- References cited in the abstract,
From a different perspective, consider gathering additional information alongside the abstract. This data can help determine the conference program session placement and select an appropriate reviewer for evaluation.
Using a powerful and flexible abstract submission form that enables effective information collection and management is crucial, as well as converting and publishing the information in a standardized, searchable, linkable, and well-organized book of abstracts.
What author information should you request in the abstract submission form?
It is typically recommended to ask for the author’s name, surname, and affiliation. The affiliation basically includes institution, department, city, and country. You may also collect the contact information of the abstract’s authors to reach out to them and invite them to participate. Incorporating these small actions can help improve the overall experience for conference organizers and attendees.
What additional questions related to the abstract's presenter you may ask?
Gathering extra information about the abstract's presenter may simplify the management process. Here are some potential questions to consider:
- Would you like to participate in the poster competition?
- Would you like your abstract to be included in the book of abstracts?
- Are you willing to serve as a reviewer for other abstracts in your area of expertise?
- Do you require any special equipment for your presentation?
How long should the abstracts be?
It is recommended to set a minimum of 200 words and a maximum of 1000 words limit for the length of abstracts. This range allows for effective evaluation of the abstract by reviewers and organizers. Additionally, this length is suitable for placing each abstract on a single page, which facilitates easy export or conversion of collected abstract submissions into a well-designed book of abstracts.
What are common mistakes authors make in abstract submissions, and how can you address them?
There are several common mistakes that authors make while submitting their abstracts, which was the main motivation of development MeetingHand abstract management solution. These common mistakes can be addressed by implementing specific strategies in the abstract submission form:
- Authors often neglect reading instructions for abstract submissions. To prevent this, set rules within the submission form to ensure abstracts are submitted in the desired format.
- Including too much or too less detail is another common mistake. Setting up minimum and maximum length limits can help resolve this issue.
- Many authors use copy-paste method to submit their abstracts without thoroughly checking them. Implementing a review process, such as "What you see is what you get," can mostly solve this issue.
- Authors may not spend enough time writing the affiliations of other authors. Collecting affiliations in multiple fields and allowing authors to edit them until the evaluation process begins can help to address this issue.
- Authors can make mistakes related to a lack of attention to detail, such as typos and grammatical errors. Implementing a review process can help minimize these errors.
- Some authors may not cover the specific requirements of the abstract's content. Collecting the abstract's content in multiple text fields, such as introduction, methods, findings, and conclusion, can help ensure that all necessary information is included.
How to notify an abstract’s author? Step-by-step checklist
Who should make the final acceptance or rejection decision, and how should they approach it?
The final decision on whether to accept or reject an abstract should be made by the chair of the conference or the scientific committee. When making the decision, consider the following steps:
- Begin with an overall evaluation to determine how many acceptable abstracts have been received in each presentation category.
- Identify the number of available slots for oral presentations, taking into account opening and closing sessions, plenary and invited talks, panels, and other presentation types.
- Create a conference program that considers session content, which may require combining related scientific topics.
- Review the recommendations from reviewers carefully, paying attention to their comments and the overall quality of the abstracts. Asking reviewers to evaluate using an "accepted, conditionally accepted, rejected" methodology will simplify the decision-making process.
- Consider the authors and their registration status before making the final decision.
Checking the registration status of the abstract's presenting author will help build a well-fitted conference program.
Keep in mind that there are only three options during the decision stage: Accepted, Conditionally Accepted, and Rejected.
How should you notify authors of their abstract's acceptance or rejection status?
Manually notifying authors about their abstract's acceptance or rejection status can be time-consuming and challenging, especially when personalizing acceptance letters with names, abstract titles, presentation types, and more.
Using an abstract management software solution, like MeetingHand, can simplify this process. It allows you to easily personalize acceptance messages by editing the content and adding abstract names, presentation types, and other relevant information. Additionally, you can track notifications about their delivery, open, and download rates or status.
It is recommended to choose an abstract management platform that enables authors to log in, track the evaluation process of their abstracts, receive requests from reviewers, and make updates when necessary.
When should you notify the authors about the abstract review results?
The notification timeline depends on the completion of the evaluation process. It's important to notify authors at least by the declared deadline. To ensure timely notifications, it's advisable to start the evaluation process early, rather than waiting for the submission deadline, especially considering that reviewers often work on a volunteer basis.
Furthermore, it's not mandatory to wait until the declared notification date to inform authors personally, especially if the number of submitted abstracts does not significantly exceed the available presentation slots.
Notifying authors early will help them plan and arrange to finance their attendance more effectively.
What should you do with canceled, unpaid, or un-presented abstracts?
To ensure smooth abstract management, it is recommended to remove canceled abstracts as soon as you receive the cancellation requests. For unpaid abstracts, it is preferable to retain them and remind the authors about the payment, until you receive confirmation and/or finalize the scientific program. It is essential to remove all un-presented abstracts from the book of abstracts and the conference program or, at the very least, mark them as "Not presented".
What information should you include in the acceptance letter?
When drafting an acceptance letter, consider including the following information:
- Start with a thank-you for submitting the abstract and mention the conference name and date.
- Clearly state the final decision and presentation type, including the abstract title, to ensure the author can confirm acceptance and prepare for their presentation.
- Include registration requirements, deadlines, and other relevant information, such as how to follow presentation instructions, to help the author plan and prepare for the next steps.
- Close the letter with a welcoming message, expressing that you look forward to their participation in the conference.
How to evaluate an abstract? Step-by-step checklist
Do you need an evaluation process for conference abstracts?
An evaluation process is essential for conference abstracts to ensure their relevance to the conference theme and the quality of the presentations for the audience. By involving reviewers and using an evaluation tool, conference organizers can efficiently assess the abstracts and confirm that they meet quality requirements, and contribute significantly to achieving the conference's objectives.
What should you consider for a well-structured abstract review process?
A well-structured abstract review and evaluation process is essential to ensure a seamless and fair assessment of conference abstracts. Here are the key components to consider:
- Evaluation form:
A simple, straightforward, and easy-to-use evaluation form encourages reviewers to evaluate. The reviewers should be able to preview the abstract including the title, topic, presentation type, and content, along with decision or scoring options and a comment section.
- Evaluation management:
It's crucial to have an evaluation system that enables decision-makers to monitor the status of abstracts, assignments, and reviewer-based progress, and also to manage the evaluation process efficiently.
- Reviewer communication:
Ensure timely reminders are sent to reviewers to encourage timely completion of evaluations and maintain open lines of communication to address any concerns or questions that arise during the evaluation process.
- Decision-making process:
Streamline the final decision-making process by providing an organized overview of reviewer evaluations and comments. This will enable decision-makers to make informed choices based on the quality and relevance of each abstract.
- Author notification:
Establish a timely and clear communication process for notifying authors of the decisions, whether their abstracts are accepted, conditionally accepted, or rejected.
Using an abstract review management tool that offers these components and the abstract database in an efficient process and easy-to-use interfaces is crucial for a seamless and fair evaluation experience for all who are involved, to ensure a successful conference program.
Will you provide reviewers with abstract review instructions?
Providing instructions and guidelines about abstract review and evaluation can help reviewers clearly understand the evaluation criteria and expectations, contributing to a successful conference program. This approach ensures that all reviewers evaluate the abstracts based on the same standards, leading to a fair and consistent evaluation process. While it may not always be necessary, especially when dealing with a limited number of abstracts or reviewers, offering guidance can still be beneficial in maintaining consistency and quality across evaluations.
How should reviewers evaluate abstracts? Using their expertise or following specific evaluation models or criteria?
Allowing reviewers to use their expertise and make an overall evaluation is often the easiest approach. However, you can also implement a more advanced evaluation process or methodology based on your requirements. Common models include SCORE (Scientific Communication Online Review and Evaluation), SADE (Significance, Approach, Data, Evaluation), QUALSYST (Quality System for Technical and Scientific Conferences), and Likert scales. These evaluation approaches typically involve scoring aspects such as relevance, quality, originality, clarity, and significance of the abstract. It's essential to consider the specific needs of your conference when deciding on the most appropriate evaluation approach.
Will you implement a blind evaluation process?
The decision to use an open or blind review process depends on the conference's objectives and requirements. A blind review, which means hiding the author's identity, can help promote fairness in the selection process for abstracts to be presented at the conference. Consider your conference's specific needs and goals when deciding whether to implement a blind or open evaluation process.
How can you encourage reviewers to evaluate on time?
Ensuring that reviewers complete evaluations on time is critical, as they are often busy, high-profile academics volunteering their time. To motivate reviewers, consider the following strategies:
- Provide user-friendly evaluation interfaces: Make it easy for reviewers to track their duties and progress by offering an intuitive and straightforward evaluation system.
- Offer clear evaluation guidelines: Help reviewers understand the evaluation criteria and expectations by providing clear instructions and guidelines for the assessment process.
- Streamline the evaluation process: Simplify the process to make it less time-consuming and more efficient, ensuring that reviewers can complete their evaluations without unnecessary complications.
- Maintain clear communication: Keep an open line of communication with reviewers to address any concerns or questions that may arise during the evaluation process.
- Send reminders and follow up: Remind reviewers of upcoming deadlines and follow up with them to encourage timely completion of evaluations.
By implementing these strategies, you can encourage reviewers in completing evaluations on time and contribute to a successful conference program.
How many reviewers should you assign to each abstract?
The number of reviewers assigned to each abstract depends on the review process being used, the number of abstract submissions, and the available reviewers. Balancing the number of reviewers with the required evaluation time is essential for a successful evaluation process. Generally, assigning at least two reviewers to each abstract can help ensure fairness and reliability in the evaluation process. However, you may consider assigning more reviewers based on the specific needs and goals of your conference.
How to create a book of abstracts? Step-by-step checklist
Will you create a book of abstracts?
Conference organizers typically prepare and publish a book of abstracts, which includes all the oral and poster abstracts scheduled for presentation. This resource offers participants an overview of the conference content and can serve as a reference in scientific studies. However, some conferences may opt to publish a book of extended abstracts or full papers instead of, or in addition to, a traditional book of abstracts.
How do you prepare a book of abstracts for a conference?
Preparing a book of abstracts for a conference involves several steps. Typically, it includes the following sections:
- Title or cover page: This includes the title, conference name, and date.
- Copyright page: Contains copyright information and an ISBN number, if required.
- Preface: Written by the conference chair, it provides an introduction or overview of the conference, including the theme, scientific scope, and objectives.
- Acknowledgment page: Includes members of the committees, invited speakers, and other parties involved in the conference.
- Table of contents: Clearly shows the sections and lists the abstracts in alphabetical order by author names or by presentation order.
- Abstracts section: Contains the abstracts, typically including the title, author's name, and affiliation, body, and keywords. Grouping the abstracts by topic, category, or in a different logical order is important and may require using sub-headers such as invited speakers, oral, and poster abstracts.
- Author Index: Lists all authors in alphabetical order, along with their abstracts' page numbers.
Preparing these sections as separate doc files and combining them into one file can save time and effort, as most abstract management tools provide. The new generation of abstract management software, such as MeetingHand, offers all abstracts in a ready-to-publish book of abstracts. However, in all cases, making a final review of the details for an error-free book of abstracts is a must, and working with an expert for editing and formatting the book might be a better decision, especially when publishing a hard copy was considered. Because, ensuring that all the necessary edits and revisions are done, and all confirmed abstracts are included in a consistent format and styling throughout the book of abstracts is crucial before publishing the book of abstracts.
How to publish, distribute, and promote a conference book of abstracts?
The book of abstracts can be published either in digital or print format, or both. Digital publishing of the book of abstracts has become more popular due to its advantages, such as wider and faster distribution, easy access, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to make seamless revisions and updates. Digital publishing is also environmentally friendly as it uses fewer resources and produces less waste. However, some conference organizers still prefer to provide printed versions, even in limited quantities, for participants who prefer physical copies and for archival purposes.
To effectively promote the conference book of abstracts, share it on the conference website, as well as on the websites of relevant organizations and associations. Email it to online repositories and digital libraries. Additionally, ensure that the book of abstracts is accessible and searchable by search engines like Google. Using appropriate keywords and relevant metadata will increase its visibility.
How to create a conference program? Step-by-step checklist
How to prepare and schedule a conference program agenda?
In the early stages of conference planning, organizers should start working on the conference agenda by creating an initial program overview or program at glance. This includes the conference schedule, session times, social activities, and other main events. Once the invited speakers and abstract authors confirm their participation and social activities are determined, the scheduling of the conference program can begin. Creating a comprehensive and well-organized conference agenda is a crucial goal.
The following steps may lead to a successful agenda:
- Calculate the total time required for invited speakers, oral and poster presentations, and opening & closing sessions.
- Add time for onsite registration and breaks, including coffee breaks and meals.
- Determine the number of presentation rooms and the duration of each presentation. Adjust the presentation time and/or the number of rooms to fit the required schedule.
- Allocate specific time frames for each session, considering presentation topics, the number of presentations on each topic, breaks, and networking opportunities.
- Assign presentations to sessions by linking speakers and abstract titles.
- Add social activities to the conference agenda to create a draft program.
- Share the draft program with speakers and all those involved in the conference for feedback.
- Ensure that all presentations are included and make any necessary adjustments.
- Finalize and release the conference program on the conference website, announce it to attendees, and promote it via social channels and to all those involved in the conference.
Grouping presentations by topic, and category in sessions, particularly when parallel rooms are being used, allows attendees to easily find presentations they're interested in and present on time. Additionally, scheduling break-out times and social activities is essential, as networking and socializing are the key motivations for attending a conference. Providing opportunities for attendees to connect and discuss presentations can significantly enhance the overall conference experience.
"What is happening outside the conference rooms is as important as what is going on inside" since it serves as a key motivator for most participants. Therefore, it's crucial to schedule breakouts and social events at the conference in a manner that fosters networking and socializing opportunities, ultimately increasing satisfaction and significantly enhancing the overall experience.
Tips:
- While it's possible to create complex abstract submission forms and require authors to write in specific formats for well-designed abstracts, keeping the process simple and concise can maximize the number of collected abstracts. This approach helps conference planners create a comprehensive program and may potentially increase attendance.
- While it's possible to request more author information like current email addresses and phone numbers, obtaining complete or accurate responses from corresponding authors may be challenging. Moreover, it's essential to consider legal rules and regulations surrounding personal data collection, such as CCPA and GDPR
- While most of the conference planners focus on defining the deadlines for abstract submission start & end-date and author notification dates, the deadline for the Authors’ payment is more important as it is required to begin scheduling the agenda and avoid presentation no-shows.
- While the number of attendees is a key indicator of event success, the number of presentations delivered plays a crucial role in determining a conference's success. To maximize the event's impact, it's essential to minimize presentation no-shows. By efficiently following up with and encouraging presenters, conference organizers can reduce no-shows and enhance the overall success of the conference.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing the abstract submission process for an academic event is a crucial task that requires careful planning, attention to detail, and effective communication with all stakeholders. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can streamline the submission process, ensure a fair and transparent evaluation process, and create a high-quality book of abstracts that showcases the best research in your field. Remember to keep your communication channels open and provide clear guidance and support to authors throughout the submission process. With these tips in mind, you can help to make your academic event a success and foster a vibrant and engaging research community.
However, we also would like to remind you that MeetingHand as a comprehensive event management software has a sophisticated abstract management module. It combines registrations with abstract submissions and helps you manage the abstract evaluation process, create your event program, create your Book of Abstracts, and even manage your invited speakers. So, should you require a complete abstract management solution, we strongly suggest you book a demo with us and attend a private demo session.